CellEnergy, now with NADH and Coenzyme Q10.
ZellEnergie consists of valuable bioactive vitamins, trace elements and polyphenol-containing natural substances.
By combining the various ingredients, ZellEnergie provides versatile support for the body's overall system.
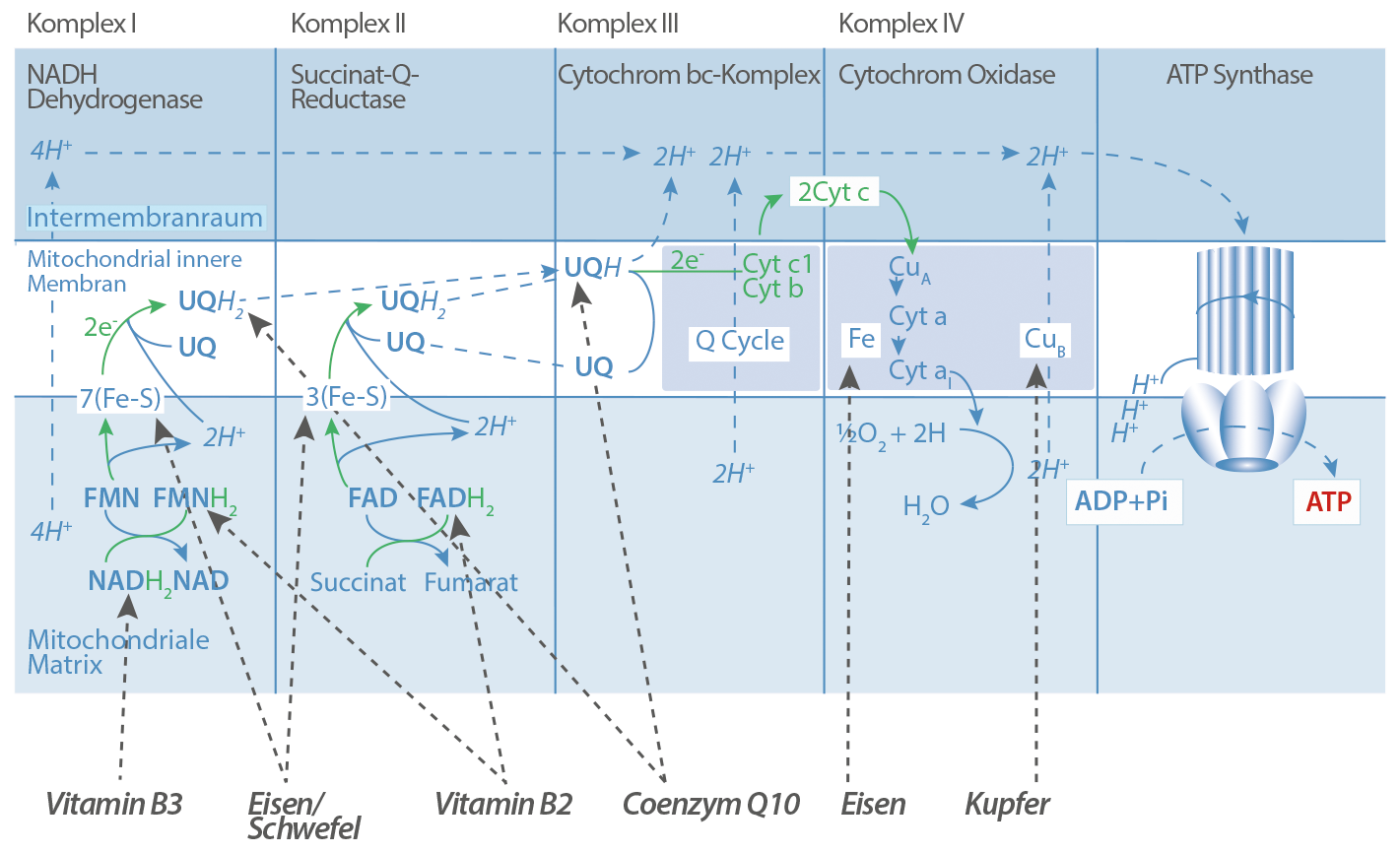
The contained vitamin B2 (bioactive riboflavin-5-phosphate) as well as the trace element copper make an important contribution as an antioxidant and promotes the protection of the entire organism.
Vitamin B3 (bioactive nicotinamide) is crucial for many metabolic processes and supports the body in building and breaking down muscles, skin and nerves.
The trace element iron is responsible for oxygen transport in the body, which contributes to the maintenance of healthy cognitive functions as well as general performance.
Developed in collaboration with Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Brigitte König.
Coenzyme Q10 - Vital Protection from Within
Coenzyme Q10 keeps our bodies fit by, on the one hand, ensuring our internal energy supply and, on the other, acting as a potent antioxidant that protects cells. This is precisely why it is interesting as a versatile anti-ageing talent that combats both internal and external signs of ageing.
A name with meaning
Why "Q"?
The "Q" refers to the coenzyme's membership of a group of organic compounds with the English name quinones. This reference to quinones is also found in the other names for coenzyme Q10, such as ubiquinone or ubiquinol. The respective first syllable "Ubi" is again an allusion to its ubiquitousness in cells.
Why the "10"?
The number in its name refers to the extent of its attached isoprenoid side chains, a natural substance group. In fact, there are different types of coenzyme Q with isoprenoid side chains of different lengths. The most common coenzyme Q representative in human mitochondria is the one with a 10-part side chain - coenzyme Q10.
What is behind coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 is a fat-soluble, vitamin-like substance, which is why it is sometimes known as vitamin Q10. Structurally, it is related to vitamin K. It is found in almost all forms of life - from bacteria to mammals. In our human tissues, it is ubiquitous and found in every single cell of our body. In 1957, it was first isolated in the mitochondria of a bovine heart.
In the service of cells
Internal cellular drive
Coenzyme Q10's ubiquity in cells serves a reason. After all, its main role is found in the cellular powerhouses, the mitochondria, as part of the electron transport system there. More specifically it participates in the redox reactions within the electron transport chain, facilitating the production of ATP, the universal energy carrier in cells, in the mitochondria.
Protecting Cells
Q10 is known for its antioxidant talents and can even outperform the prominent free-radical scavengers vitamins E and C. Its antioxidant efficacies come into play particularly in plasma membranes and lipoproteins, among others. Its antioxidant protection also includes strengthening the presence of other free radical scavengers in the body. Thus, it maintains both ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol in their respective reduced forms. In other words, it ensures that vitamin C as well as vitamin E are present in their most biologically active variants.
Stop sign for age-related ailments
As we get older, both the mass and the strength of our muscles decrease. The process starts somewhat from the age of 30
Natural Boost
As an energy supplier to the cells, coenzyme Q10 can support our body's own energy supply accordingly. Taking coenzyme Q10 can therefore provide relief from symptoms of fatigue and increase our performance. In this respect, it offers benefits not only to athletes.
Supply of coenzyme Q10
Body's own production
Main source of coenzyme Q10 is our own body. It is produced in all cells involving a multiprotein complex of mitochondria. Since our own production decreases with age, this unfortunately results in the problem that our most important supply pathway is increasingly impaired accordingly.
Food
Rich in coenzyme Q10 are foods such as meat, fish, nuts and various oils. To a lesser extent, dairy products, vegetables, fruits and cereals also serve as sources. On average, we consume only 3 to 6 mg daily. Its poor water solubility is problematic, which means that it is often absorbed slowly and incompletely in the intestine and thus has a low bioavailability.
Supplements
Due to its somewhat problematic bioavailability, intake via dietary supplements is particularly suitable for replenishing its stocks. The intake of coenzyme Q10 supplements:
- effectively increases the stock of the coenzyme in the tissues
- should be taken together with food due to its fat solubility. This increases intestinal absorption threefold
- is considered safe and free of side effects in doses up to 1200 mg/day
Did you know? Coenzyme Q10 ranks #3 among the "Most Taken Supplements" in the U.S.
Deficiency
The body of a healthy adult contains an average of 0.5 to 1.5 g of coenzyme Q10. However, these stocks can be adversely affected by a number of factors. The main factor here is the natural ageing process.
Generally, the stock of Q10 in our bodies decreases as we grow older. Our ability to produce it ourselves begins to dwindle from the age of 20 - and by the age of 40, our coenzyme Q10 stocks begin to decline rapidly.